Each year, 100,000 people visit their doctor with abdominal pain, with approximately 30,000 of them diagnosed with gallstones. The standard treatment for these patients is a laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Since the 1990s, the number of surgeries has increased exponentially, despite the lack of clear international criteria.
As a result, gallbladder removal is one of the most common surgeries in the Netherlands, yet it is not always effective against pain: about one-third of patients continue to experience abdominal pain after cholecystectomy. The procedure has long been an example of inappropriate care, but this is now changing.
In a 2019 study conducted by Radboud university medical center, patients with abdominal pain due to gallstones were divided into two groups. One group received the standard treatment of cholecystectomy, while the other group received a restrictive selection strategy, with surgery considered only after evaluating various pain symptoms. The number of surgeries in the restrictive strategy group decreased, but one year later, one-third of patients in both groups still had abdominal pain.
Based on this study, researchers recommended caution with cholecystectomy in patients with gallstones and abdominal pain.
Five-year follow-up
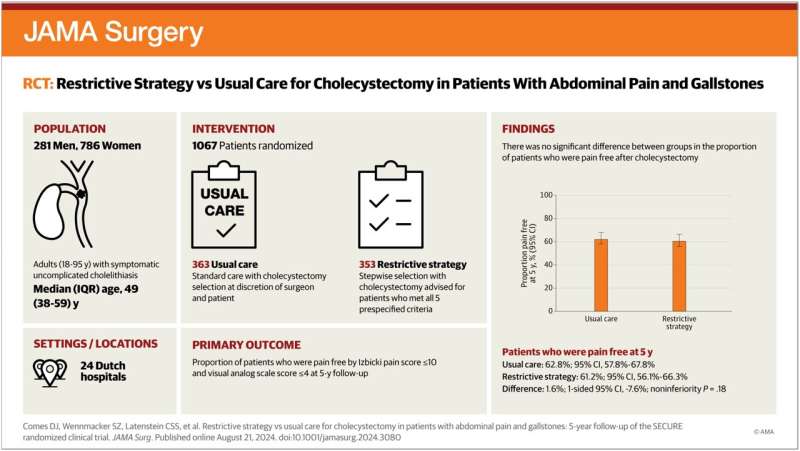
The researchers re-evaluated the patients five years later. The results of this study conducted in 24 Dutch hospitals are now published in JAMA Surgery. Daan Comes, physician-researcher and lead author, explained, “We wanted to investigate the long-term effects of a restrictive strategy to this surgery in this group of patients. Therefore, we contacted over a thousand patients by phone. They completed questionnaires, and we reviewed their medical records.”
What did they find? The number of patients with pain had not decreased over the years: still, only two-thirds of the patients were pain-free. However, the restrictive strategy approach led to fewer unnecessary cholecystectomies.
“In the restrictive selection group, we did not observe more complications from gallstones or surgery than in the other group. It seems that a restrictive selection strategy is feasible, but only for the right patients,” Comes added.
Better selection criteria
For better insight into identifying the right patient group, Radboudumc developed a decision rule in 2021 based on scientific research and patient data. Surgeon and principal investigator Philip de Reuver stated, “It was found that intense, episodic pain is a strong indication for surgery. Additionally, a previous abdominal surgery or the presence of other symptoms, such as bloating, heartburn, and persistent pain, are reasons to be cautious about surgery.”
With this knowledge, doctors and patients can make better-informed decisions. “Patients with recurrent biliary colic certainly benefit from this surgery. However, more than a third of patients with gallstones also have symptoms of dyspepsia and irritable bowel syndrome. In those cases, this surgery is not helpful. We should really rule out these conditions before proceeding with a cholecystectomy,” said de Reuver.
Therefore, De Reuver is starting a follow-up study on the effect of a lifestyle intervention in patients with abdominal pain and gallstones, where the decision rule indicates that surgery would have limited benefits. He expects the lifestyle intervention to improve patients’ health, quality of life, and reduce pain.
“In the Netherlands, about 65 patients undergo gallbladder surgery every day. That’s a bus full. If we can reduce that number, we save costs and capacity while maintaining the quality of life. That’s fantastic,” said De Reuver.
More information:
Restrictive Strategy vs Usual Care for Cholecystectomy in Patients With Abdominal Pain and Gallstones, JAMA Surgery (2024). DOI: 10.1001/jamasurg.2024.3080. jamanetwork.com/journals/jamas … /fullarticle/2822575
Citation:
Cholecystectomy not always necessary for gallstones and abdominal pain, study finds (2024, August 21)
retrieved 21 August 2024
from https://medicalxpress.com/news/2024-08-cholecystectomy-gallstones-abdominal-pain.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.

