A research team has successfully induced self-location illusions with multi-sensory virtual reality (VR) in an MRI scanner and observed corresponding changes in the human brain’s grid cell activity.
The paper is published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
The brain is known to contain grid cells and place cells, which perform global positioning system (GPS) functions that allow us to recognize where we are. While traveling to a specific place, the GPS cells along the way fire in turn, depending on their location, and these cells play an important role in recognizing our location in the form of coordinates and remembering events in space.
Humans can sometimes perceive themselves to be in a different location without actually moving their physical bodies, such as during an illusion or an out-of-body experience. However, such purely cognitive self-location changes—and the corresponding response of the brain’s GPS cells—have not been investigated in animal models like rats, where these perceptions cannot be induced or confirmed.
Furthermore, conventional methods to study GPS cell studies have required opening the skull and measuring the activity of individual cells in the deep brain structures with invasive electrodes, limiting our understanding of human GPS cells.
-
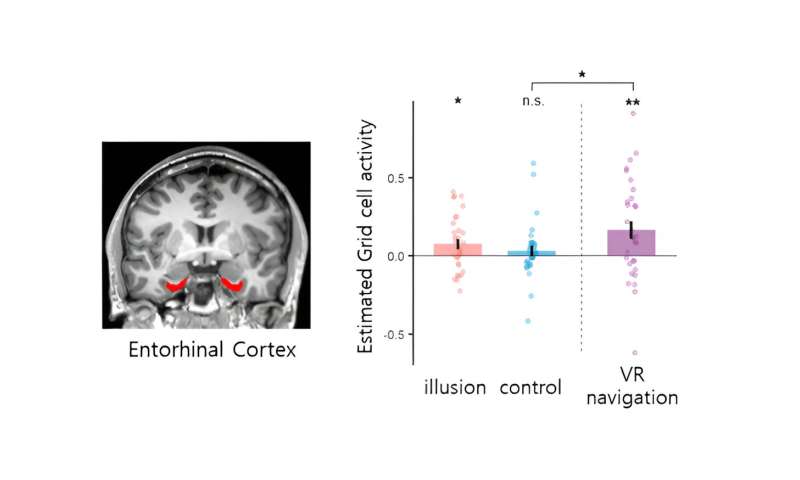
Grid cell activities in the Entorhinal cortex during different task conditions. Credit: Korea Institute of Science and Technology
-
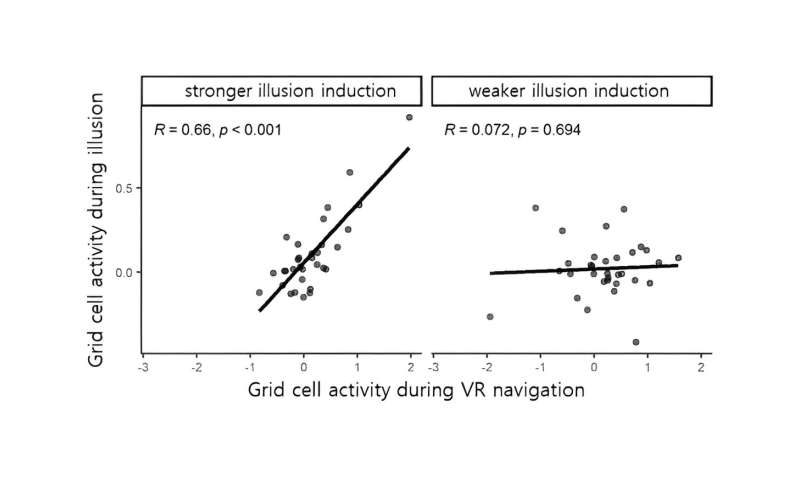
Similarity between illusion-induced and VR navigation-induced grid cell activity. Credit: Korea Institute of Science and Technology
To observe grid cell activity during the illusory self-location changes, the researchers combined MRI-compatible VR technology with multisensory bodily stimulation to induce the illusion, which was precisely controlled in various directions as designed.
The fMRI Images measured during the experiment were used to estimate the activities of grid cells, and the subjective illusory experiences of participants were assessed through post-experiment questionnaires and behavioral metrics reflecting their perceived self-location.
As a result, the team demonstrated for the first time that purely cognitive changes in magnetic position such illusory self-location changes induced by multisensory bodily stimulation, without any changes in the visual environmental cues, elicit corresponding activities of human grid cells.
This is the first clinical study to demonstrate that multisensory bodily stimuli alone can evoke grid cell activities, without any kind of navigation (not active nor imagined) and without change in the visual perspective.
It shows that GPS coordinates in the human brain respond not only to the physical location of the body but also to location information based on various cognitive activities and experiences, raising the possibility of objective diagnosis of hallucinatory symptoms through brain image analysis.
The findings are also expected to contribute to the development of new therapies by providing targets for the treatment of patients suffering from illusory symptoms such as out-of-body experience.
The research team included Dr. Hyuk-June Moon from the Bionics Research Center at the Korea Institute of Science and Technology (KIST), in collaboration with Prof. Olaf Blanke’s team at the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology Lausanne (EPFL).
Dr. Moon said, “Unlike previous human grid cell studies, which have relied on changes in visual environmental cues from a first-person perspective, we have newly suggested a key research element of integrating multisensory bodily signals.”
“We plan to conduct follow-up international collaborative research to further understand the brain mechanisms underlying illusions caused by various mental and neurological diseases, and to develop non-invasive brain stimulation treatments that can alleviate these symptoms.”
More information:
Hyuk-June Moon et al, Changes in spatial self-consciousness elicit grid cell–like representation in the entorhinal cortex, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (2024). DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2315758121
Citation:
Tricking the brain’s inner GPS: Grid cell responses to the illusion of self-location (2024, May 20)
retrieved 20 May 2024
from https://medicalxpress.com/news/2024-05-brain-gps-grid-cell-responses.html
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no
part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.

